Uses and Limitations of Software Bots
There are many misconceptions surrounding software bots. The term ‘bot’ is applied to a vast array of different technologies, which can make pinning down a precise definition difficult. Clearly the pervasiveness of software bots speaks to how useful they can be. But what exactly are software bots, and what exactly are their capabilities? More importantly, do they have a place in the technological toolbelt of the workforce of tomorrow?
What Are Software Bots?
Software bots can take several different forms, but in general they are computer programs that simulate human activity to automate tasks. Typically, these tasks are simple, repetitive, and routine, and as such a software bot can perform them quicker and more efficiently than a human could.
In essence, a software bot is an IT tool to support, simulate and sometimes even replace human work.
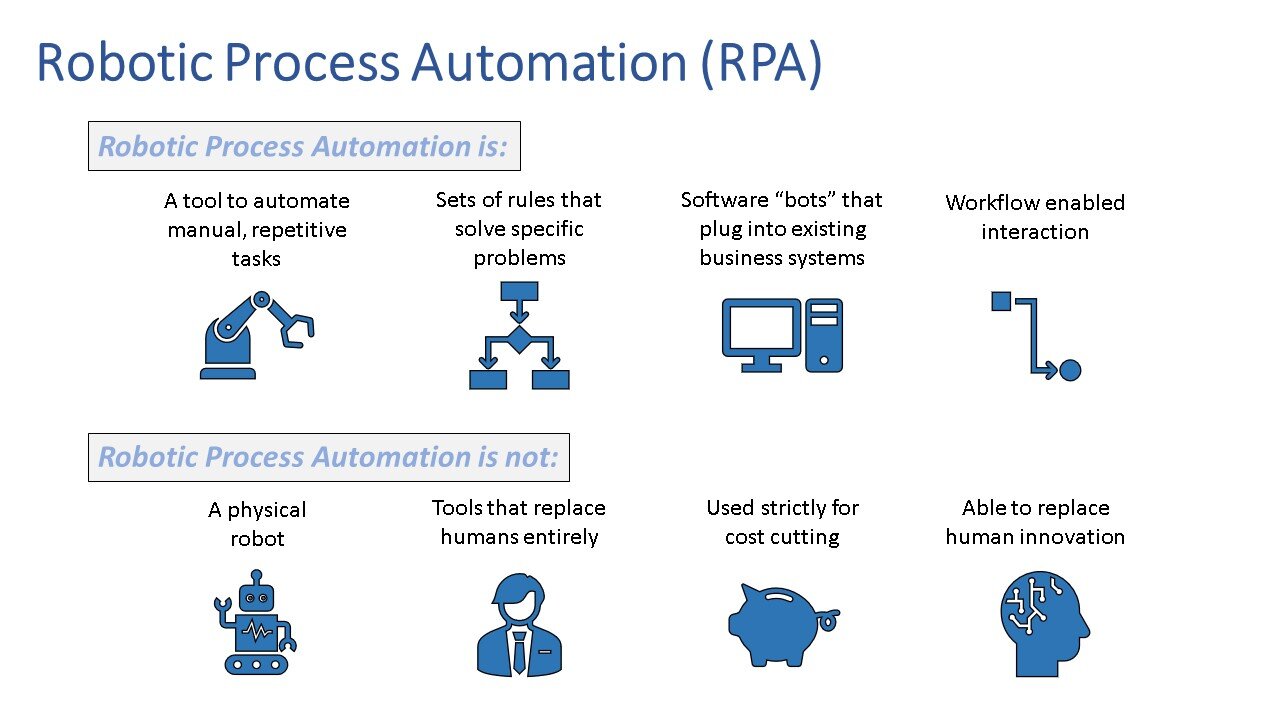
Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the technology that allows for configuration of software bots to emulate the actions of a human executing a business process. This is the type of software bot that accountants are likely the most familiar with in a professional capacity.
For traditional software bots, a software developer produces a list of actions they want to automate then builds a program to interface with a system through its back-end. In contrast, RPA bots let users utilize a front-end interface to capture processes to automate, allowing less technically-inclined employees to create bots. These RPA bots can then interpret and trigger responses and communicate with other systems in order to perform a variety of repetitive tasks.
RPA bots are capable of mimicking many human user actions. They can log into applications, move files and folders, copy and paste data, fill in forms, extract data from documents, scrape browsers, and more. This automation empowers accountants to spend their time on other activities by expediting repetitive tasks, in some cases removing those tasks altogether.
Limitations of Software Bots
RPA bots are relatively easy and quick to implement and can provide a strong return on investment, but many examples of failed RPA projects exist that can be used as a metric for setting realistic expectations. Bots can be very impactful tools, but there are limitations to consider before diving headlong into an implementation.
Understanding Use-Cases
A common misstep is the misuse of the word “process,” in robotic process automation. Bots are purposely designed to automate tasks, not to fix end-to-end business processes. RPA bots must be placed on top of robust and streamlined processes in order to be transformational. Automating the processes of a bad software platform will still get you to the wrong answer, just faster.
Software bots are not always the answer. They leverage human-to-machine processes to allow users to perform their work faster, but perhaps not as quickly or efficiently as they would with a different software service or a well thought-out and controlled business process.
Magnifying Problems with Underlying Software
The fact that RPA bots layer on top of existing systems and directly integrate into a company’s current infrastructure is a double-edged sword. Such a relationship removes the need for invasive changes to underlying systems because the business logic of the system is untouched. On the other hand, if there are any weaknesses of the software being automated then a huge liability is being generated. Errors that arise from poor software are an annoyance to human users, but are truly crippling to software bots that are too rigid to adapt to unexpected errors. If the system is broken, a bot will accelerate the problem.
Change Management Complications
By the same logic, because software bots mimic human behavior in a static way, they lack a human’s ability to adapt to change. If bots are added to systems that will be changing over time, the systems will require regular updates to the associated RPA bots. Any change to the underlying system will necessitate a new set of instructions for the bots running against it. This can greatly impact the speed with which change can be enacted.
Operational Risks
Leveraging bots also presents operational risks. Just because bots perform processes systematically does not mean they will never be wrong. Unlike a human, a software bot does not know instinctively when something goes wrong and will not stop to ask questions. There will be bugs that go unnoticed and that can compound into operational failures. It is essential to have checks and balances with human oversight in place.
Security Risks
Security is also a concern with bots that needs to be acknowledged. RPA bots that are not well controlled will open the door to unauthorized, automated changes that go undetected. The access that bots require to software code poses a risk of noncompliance, data breaches, and other threats. Because of the high processing capability of RPA bots, nefarious actions will have a greater chance of being processed before the threat is mitigated.
Employee Resistance
Many businesses looking to build software bots are met with employee resistance. Employees’ concerns about being replaced by robots are legitimate. The best way to view RPA bots is as a tool, not a replacement for individuals. The value comes from automating the repetitive, everyday tasks and allowing staff to focus on higher value and more interesting work. Humans are by nature habitual, and any change in the organization is likely to cause stress to the employees.
Data Interpretation Issues
Software bots require structured (or at least semi-structured) data to function correctly, but a large portion of enterprise data is buried in unstructured documents. Emails, work orders, and invoices are all examples of data that comes in a wide variety of formats. Unstructured data is an issue for bots, so other tools must be used to structure the data before it gets to them. Almost all businesses still have some form of handwritten documents on their records, and this will continue to be kryptonite to software bots until text conversion software solutions are perfected.
How Bots Can Fit into Your Business
The future of workplace productivity will require employees to work within standardized, optimized business processes. Most of the processes are well-defined, understood, and can be automated. In other cases, processes are considerably messier. Growing organizations must identify and mitigate the above issues early in the timeline of software bot implementation so that an incorrect approach will not allow workflow automation to perpetuate your current operational challenges.
Software bots should not be used in isolation; they are a tool in a toolbox. Though they have an immense amount of uses, software bots alone will not modernize an organization’s processes.
How Lucasys Is Ready to Help
Though RPA bots do have a place within enterprise organizations, they will never be a replacement for high-quality software. The Lucasys suite of software solutions is built to give users the flexibility to organize and display data in a simple and customizable way, allowing processes to be enhanced and sped up without giving up any control or oversight over business processes.
Our knowledgeable team of consultants has the experience to restructure and standardize tax and accounting systems to adapt to the growing needs of the enterprise. For organizations looking for insight on building out their software portfolio with the latest tools available to the industry, Lucasys has the solutions. To learn more about how Lucasys can help, visit https://www.lucasys.com/solutions.